
Astronauts cannot burp in space.
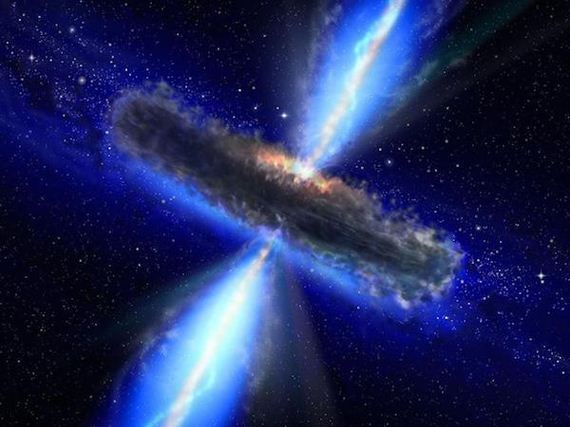

Two teams of astronauts have discovered a large reservoir of water floating in space that is the equivalent to 140 trillion times the water of our ocean. The water is in a cloud around a huge black hole that is in the process of sucking in matter and spraying out energy (such an active black hole is called a quasar), and the waves of energy the black hole releases make water by literally knocking hydrogen and oxygen atoms together.
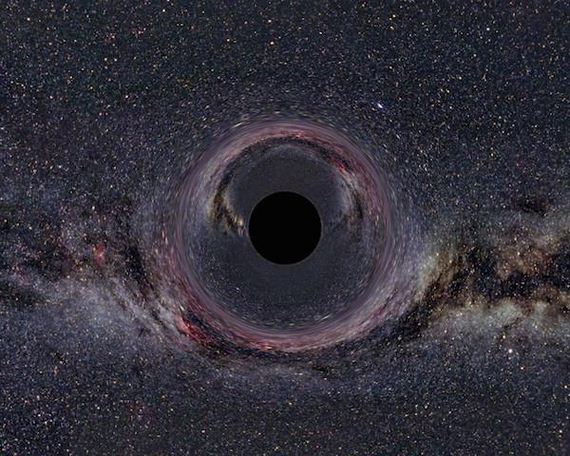

We are aware of only 14 black holes in space.

There is an unfathomable amount of stars in the known universe. An Australian University study estimated that there is around 70 sextillion. Just to reiterate – that’s 70,000 million million million. Or 70,000,000,000,000,000,000,000.

Astronauts typically gain two inches in height while in space. Due to the lack of gravity, the spines of astronauts elongate by up to three percent while they are in space. This is a similar effect to what happens while you sleep as less gravitational force is being applied to your spine while you lie down which is why we are fractionally taller when we wake up as opposed to going to bed.

It takes the average photon 170,000 years to travel from the sun’s core to the surface.

It takes that same photon only 8 minutes to then reach Earth.

A light year is the distance covered by light in a single year, this is equivalent to 6 trillion miles.

According to astronauts who have returned from space missions, space smells like a mixture of hot metal, welding fumes and seared steak.
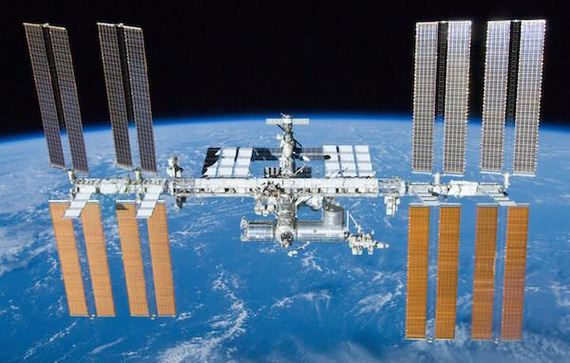
At $150 billion, the International Space Station is the most expensive object ever built. At the size of a football field, the International Space Station is only as roomy as a five-bedroom house, and travels at a speed of 17,500 mph. This means that Astronauts onboard the International Space Station view fifteen sunrises and sunsets every 24 hours.

A tablespoon of a neutron star would weigh about 10 billion tons.
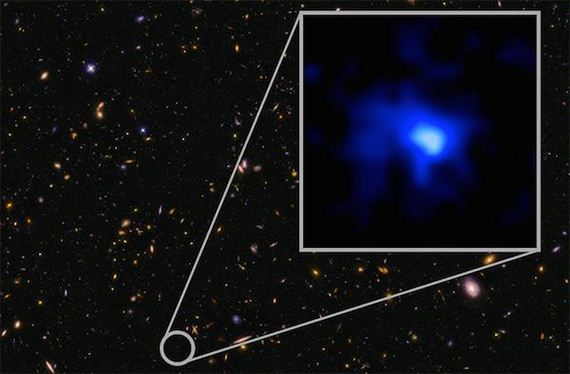
The farthest confirmed galaxy to date is called EGS-zs8-1. Imaged here, by the Hubble Space Telescope, the galaxy lies about 13.1 billion light years from Earth.
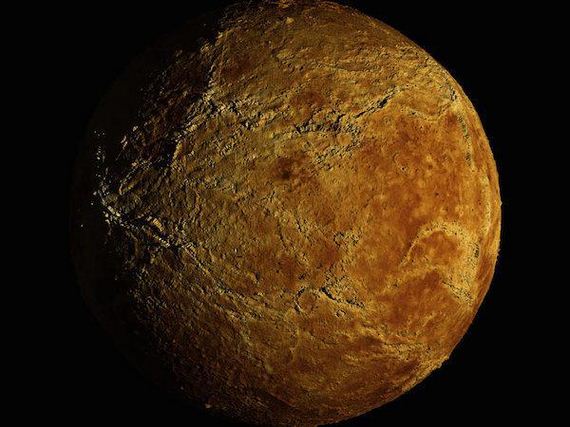

The weather on Venus is extreme. The entire atmosphere of the planet circulates around quickly, with winds blowing as fast as 360 kilometers/hour. Cloud systems can travel around the planet completely in about 4 days. The winds blow in a retrograde direction, and are the fastest near the poles. As you approach the equator, the wind speeds die down to almost nothing.
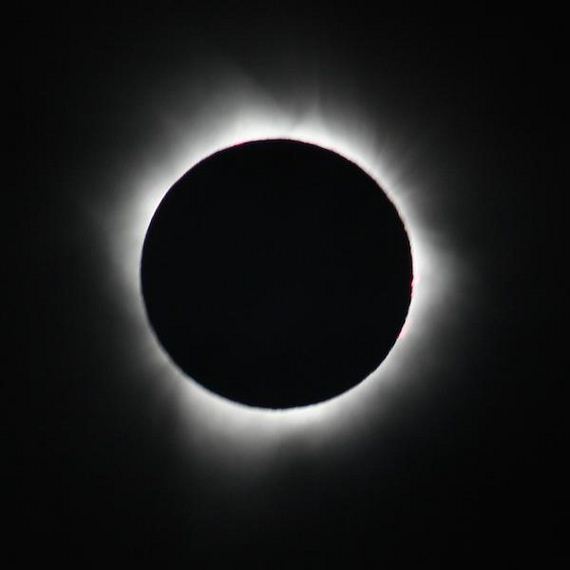

Due to an amazing coincidence of the Moon being 400 times smaller, and 400 times closer than the Sun, they both appear to be the same size.
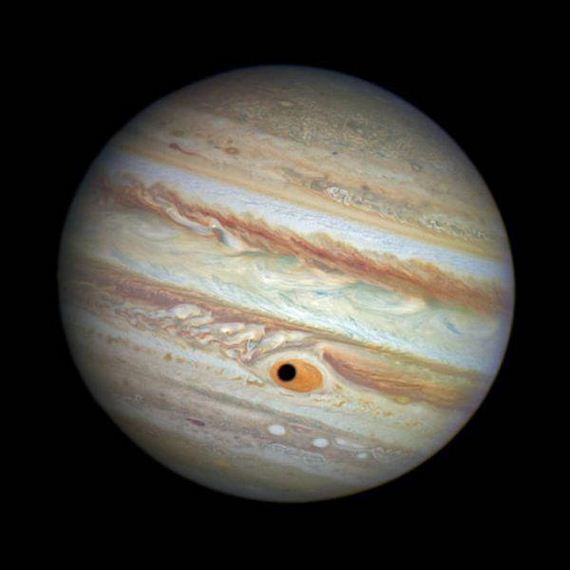

Jupiter is two and a half times larger than all the other planets in the solar system combined.

You can see another galaxy with the naked eye: The Andromeda Galaxy, 2.2 million light years away.

Last August NASA scientists offered a first look at a peculiar class of stellar wallflowers called Y dwarfs. Unlike typical stars, which burn steadily at thousands of degrees, the warmest of these Jupiter-size objects are just hot enough to bake cookies, and the coolest barely break room temperature.

The largest asteroid ever recorded is a mammoth piece of space rock named Ceres. It is almost 600 miles in diameter, and by far the largest in its asteroid belt. So large in face, that it accounts for a third of the belt’s mass. The surface area is approximately equal to the land area of India or Argentina.

The Sun travels around the galaxy a journey of 100,000 light years once every 200 million years.

The core of a star reaches 16 million degrees celsius. A single grain of sand this hot would kill a human from 150km away.
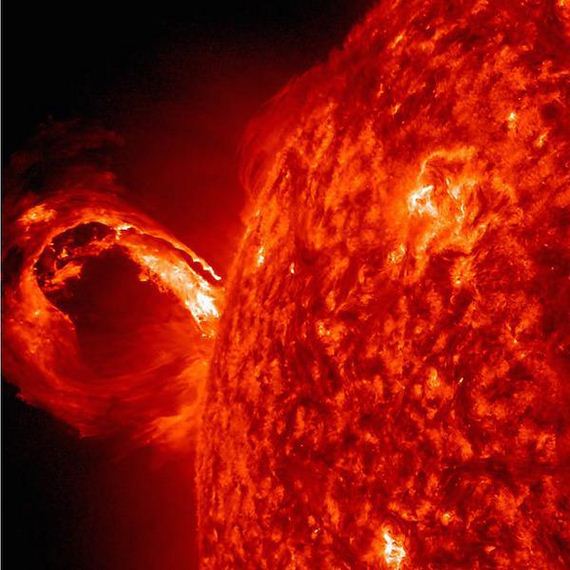

The Sun is so dense that it accounts for a whopping 99% of our entire solar system’s mass. That’s what it allows it to dominate it gravitationally. Technically, our Sun is a “G-type main-sequence star” which means that every second, it fuses approximately 600 million tons of hydrogen to helium. This means that it also converts about 4 million tons of matter to energy as a byproduct

There is a bizarre phenomenon that scientists call gravitational lensing which happens when gravity bends light to the point that objects appear in a different location to where they actually exist. A solitary black hole betrays its presence solely through gravity, which bends and warps the light of more distant objects.
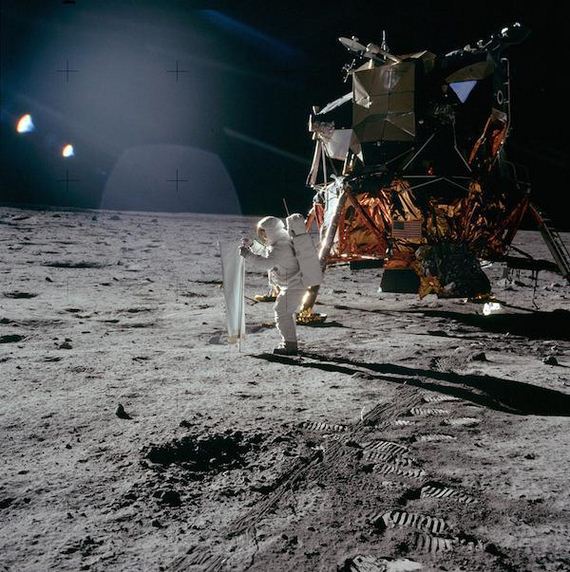

Because there’s no atmosphere on the Moon, the 1969 footprints by Apollo 11 are still there today, and will likely remain there for many, MANY years.

Earth can be seen as a pale blue dot in the picture above – 6 billion miles away. This photograph was taken by Voyager 1 in 1990 at a distance of 6 billion kilometers away. In the picture above, Earth is sized at a fraction of a pixel (0.12) against the vastness that is space. Even from within our own solar system, this picture provides some insight into how small we are in the cosmos.


Leave a Comment